Findings from Olden 2002, Predictive models of fish species distributions: a note on proper validation and chance predictions, points to that fact that there is a critical need for a method to evaluate whether or not SDM predictions would differ from what would be expected from chance alone. This paper provides a null-model in an attempt to address the ideas outlined in Olden 2002. Researchers point out that a major drawback to AUC in pseudo-absence approaches is that the AUC value indicating a perfect fit is not 1 but instead 1-a/2. Where a is the fraction of the geographical area of interested covered by a species’ true distribution which is typically an unknown quantity.
Developing the null model for evaluating AUC estimates.
- Determine the AUC value of the real SDM from provided data.
- Generate a null model by randomly collecting localities without replacement from the target species supposed distribution area.
- The number drawn is equal to the number of occurrence points within the data set.
- Repeat this process until you are able to draw a stable frequency histogram of AUC values.
- Compare the expected real AUC value against the histogram of null based AUC values and determine the probability value. Use a one sided 95% confidence interval to evaluate your real AUC value.
One potential benefit of the proposed method is that it doesn’t require the researcher to split their data set into training and test data sets. However, major assumption is that all occurrence localities are sampled equally. If this assumption is not met then the developed null model may be biased in favor of the heavily sample locations.
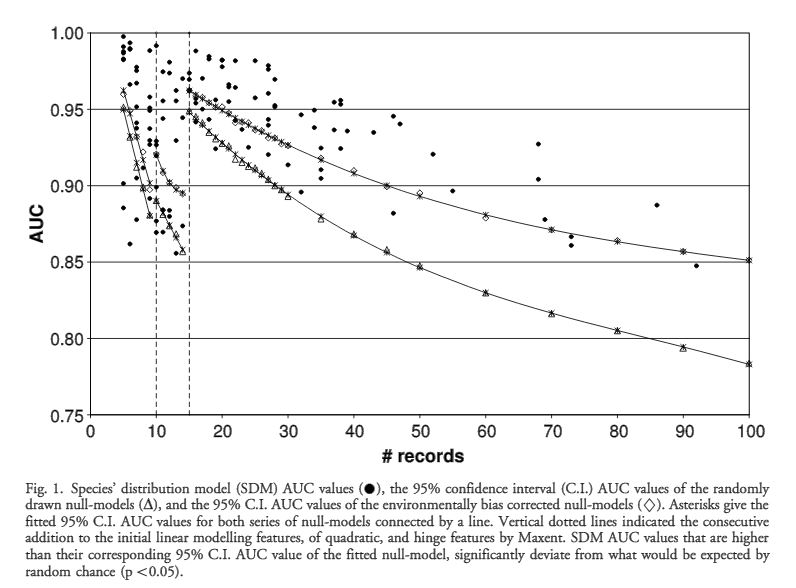
Researchers demonstrated the effectiveness of their null-model by way of case study using the occurrence records of plants from the genus Shorea. The SDM selected was MaxENT with a list of environmental data sources. Results are able to demonstrate how null models that better correct for environmental bias often produce lower AUC values than their traditional MaxENT counterparts (Fig. 1).