Climate change, biodiversity loss, and the spread of infectious diseases are three major challenges for planetary health. We know from major reports such as the…
As infectious disease modelers, one of the greatest challenges we face is in accurately reflecting the complexities of transmission, particularly human behavior. Important factors we…

Natural disasters like hurricanes, droughts, and floods are becoming increasingly frequent and severe as a result of global climate change and human activities. Perhaps more…
The control and prediction of emerging pathogens are major challenges for the health and safety of the public, as they are among the most unpredictable…

Transmission trees describe who infected whom during outbreaks of infectious diseases (see example tree below). These data are routinely collected through resource intensive methods including…

Schistosomiasis is a parasitic disease that impairs the physical and cognitive development of more than 200 million individuals globally, as a result of physiological disruptions…

Second order statistics such as variance and autocorrelation can in principle provide early warning of disease (re-)emergence. Such statistics can detect the approach to an…
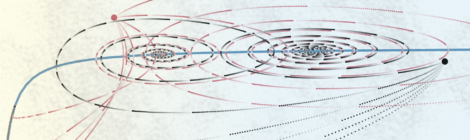
The prevalence of a pathogen emerging in a population varies in a complex manner that is difficult to model and predict, due in part to…
Effective public health efforts require an accurate understanding of which virus species are capable of spreading between humans or may develop this ability in the…
Host-parasite networks are built from a vast number of interactions, which may change seasonally or based on host densities. This combination of complexity and uncertainty…